Electro Deionisation (EDI) and Water Demineralization
Water is a natural solvent and can dissolve many elements including gases from the air. It is therefore very hard to find ‘pure’ water under natural conditions, and special techniques must be employed to remove dissolved Ions from the water.
‘Pure’ water is measured by its resistivity in MegaOhm’s with 18.2 mOhm’s (0.056µS) being ‘pure’ water. Electro DeIonisation (CEDI) is a continuous process used to produce pure and ultra-pure water using Special Ion selective membranes, Ion exchange resin and Electricity.
How it works
Electro-DeIonisation consists of Cation and Anion resins, sandwiched between layers of Cation and Anion selective membranes.
An electric current (D.C.) is passed across the bed, and the charged Cation and Anion particles flow towards their opposite charge. The resin beads help the particles to flow across the water streams.
Once the particles pass through the selective membranes, they are trapped within the resins and flushed to drain.
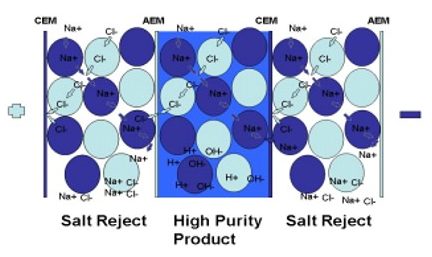
Excess electrical current is used to split water molecules into H and OH, which then regenerate the resins. The purified water flows through the center channel and out of the unit to be used.
PRE-TREATMENT
To ensure quality water and reliability, good quality pre-treatment is required using Activated Carbon, Water Softeners and Reverse Osmosis. Typically a CEDI unit needs water with less than 0.1 ppm Chlorine, less than 1 ppm Hardness and less than 10uS.
Typical uses of Pure Water
EDI produces ‘pure’ water that is free from contamination, Virus’ and Bacteria.
This ensures your test results are not tainted by water used for dilution or from dirty test equipment.

High pressure boilers and steam turbines demand the highest quality of water to prevent scale and corrosion.
Using an EDI can reduce harmful Silica and Sodium deposits meeting the TRD 401 boiler water standards.

Washing circuit boards is a common process in the electronics industry, to remove debris and excess flux or it will cause corrosion and longevity issues.
Using an EDI can produce ‘Pure’ water that is ‘non-conductive’ meaning that it can safely be used to wash circuit boards and sensitive electronics.
EDI produced water is virtually free of any contaminants and the EDI process is able to neutralise any bacteria and virus’.
The pure water produced can be used to supply WFI (Water For Injection), distillation stills or to manufacture medicines.